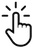I - The 1787 Constitution
|
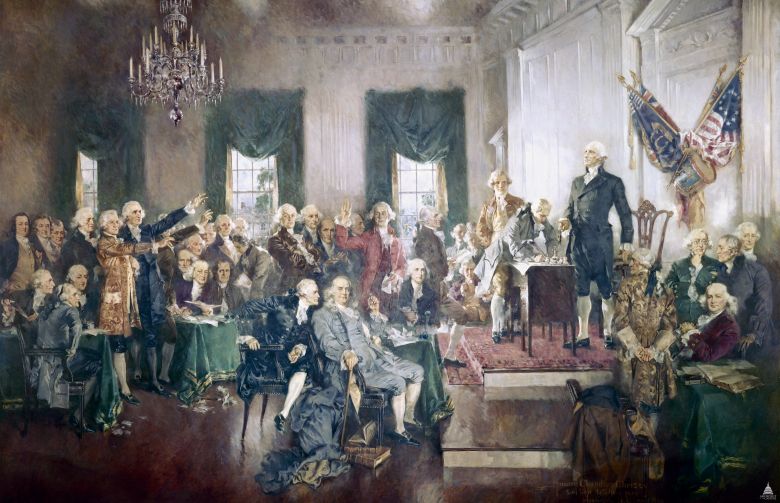
Scène à la signature de la Constitution des États-Unis, par Howard Chandler Christy. Ce tableau représente les 33 délégués qui signèrent la Constitution.
In France, The National Convention was a single-chamber assembly in from September 20, 1792, to October 26, 1795, during the French Revolution. The choice of the term "Convention" was inspired by the American Convention of Philadelphia.
|
A first Constituion was drafted between 1777 and 1781 (Articles of Confederation). However, it appeared to be inadequate (/ɪnˈædɪkwət/), for each state continued to enforce their own legislation. As a result, the laws were very different in each of the newly independent nation. The country needed a stronger federal govenment (central governement). In September 1786, each state decided to work on a new constitution.
The members of the United States Constitutional Convention (1787) drew much of their inspiration from the works of French and British philosphers such as Montesquieu and Blackstone. The United States Constitutional Convention advocated for : 1- la séparation des pouvoirs législatif, exécutif et judiciaire. 2- le bicamérisme (2 chambres au parlement: Sénat + Chambre des Représentants) 3- La primauté des lois nationales sur celles des états. Dit autrement, les lois élaborées à Washington l'emportent sur les lois spécifiques à chaque état. According to Montesquieu, this guaranteed a solid balance of power in the governement : "Pour qu’on ne puisse pas abuser du pouvoir, il faut que, par la disposition des choses, le pouvoir arrête le pouvoir." |
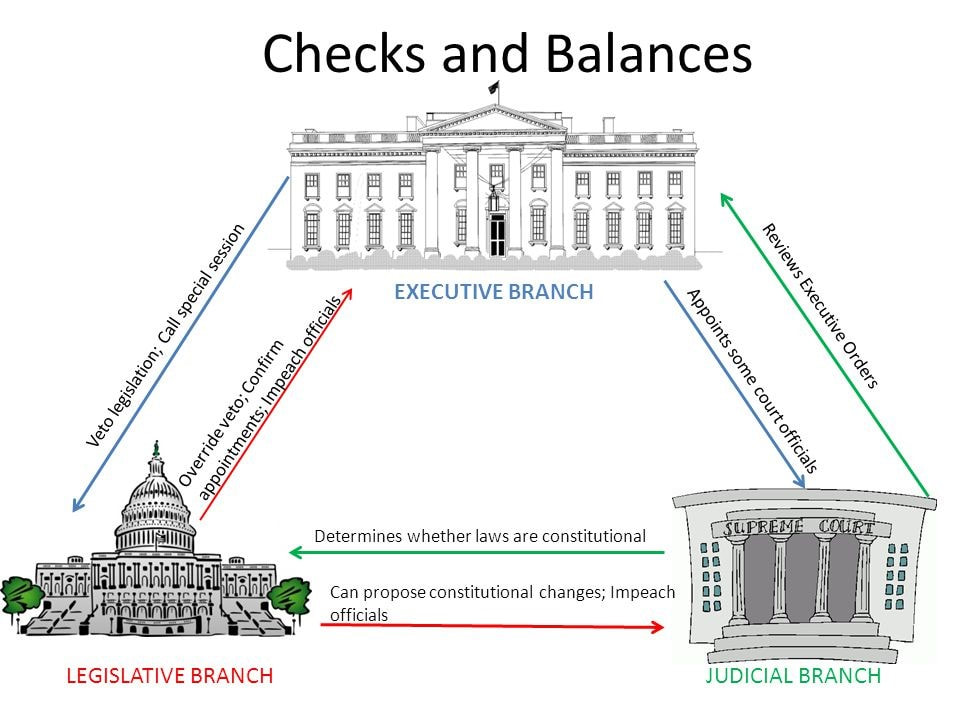
The Constitution of the United States was draftet in 1787 in Philadelphia (then the capital city of the United States). It embraced the principles advocated by Montesquieu : the separation of powers (leglisative, executive and judiciary). This is called "The Checks and Balances".
La doctrine des checks and balance
|
Cette théorie de Montesquieu a fortement inspiré les rédacteurs de la Constitution américaine. Afin d’éviter que chacun des pouvoirs n’abuse de ses prérogatives, les constituants américains ont ainsi prévu un strict partage des compétences entre organes fédéraux et États fédérés. Ils ont également réparti le pouvoir législatif entre deux assemblées, donné au Président un droit de veto sur les textes législatifs, et reconnu parallèlement au Sénat la faculté de s’opposer aux nominations relevant du Président ou encore aux traités internationaux négociés par l’administration.
Ci-contre Montesquieu
|
Should the United States opt for a strong central governement ?
Hamilton vs. Jefferson
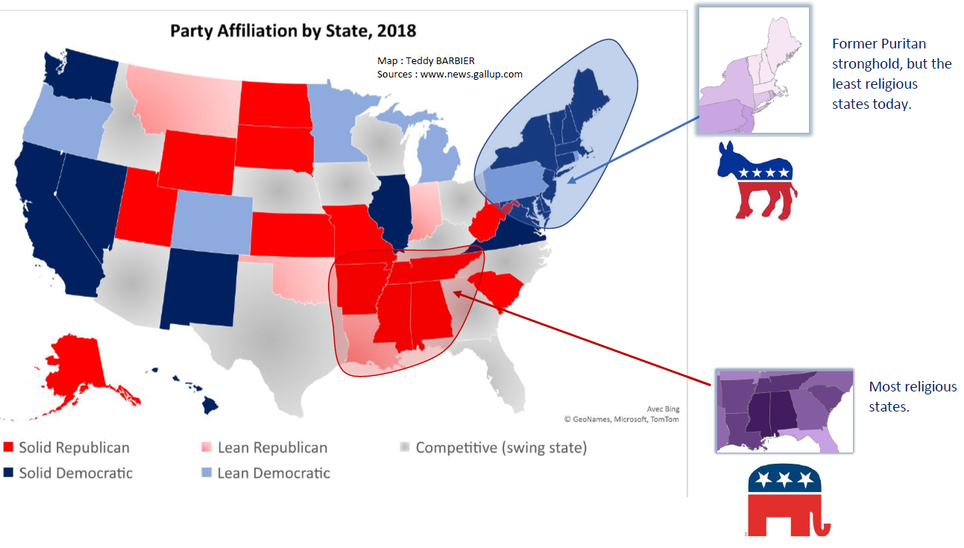
This was a hot debated issue in the 1790s between the Federalist (in favour of a strong Federal Governement) and the Antifederalist (in favour of a weak central governement). The debate between the two concerned the power of the central government versus that of the states, with the Federalists favoring the former and the Antifederalists advocating states' rights. Antifederalists equated strong central governement with tyranny.
|
Jefferson wanted the federal governement to have limited powers because he considered a strong central governement to be an "obstacle to freedom and to individual rights". |
The Federalists, favored the creation of a strong federal government that would more closely unite the states as one large, continental nation. They tended to come from the wealthier class of merchants and plantation owners. |
In the ratification debate, the Jeffersonians opposed to the Constitution. They complained that the new system threatened liberties, and failed to protect individual rights. The Anti-Federalists weren't exactly a united group, but instead involved many elements. Although the Anti-Federalists were unsuccessful in the prevention of the adoption of the Constitution, their efforts were responsible for the creation and implementation of the Bill of Rights.
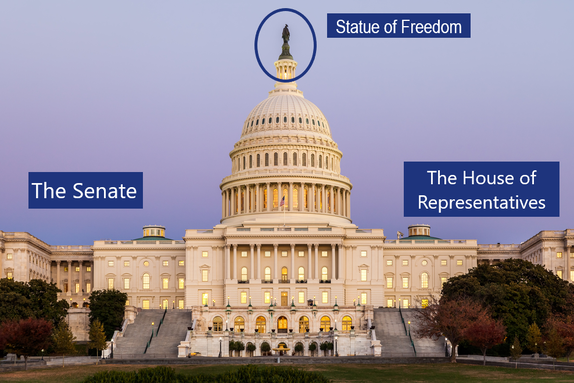
United States Congress
|
Le Congrès américain est composé de deux chambres: Le Sénat et la Chambre des Représentants. C'est ce que l'on appelle un parlement bicaméral (comme Westminster à Londres).
|
Fonctions du Congrès : Il est chargé d'élaborer, de discuter, d'amender et de voter les lois. Il possède aussi un droit de regard sur le budget du pays, le commerce et la défense.
The Supreme Court
|
|
The American Political Parties
|
The Democratic Party is generally associated with more progressive policies. It supports social and economic equality, favouring greater government intervention in the economy but opposing government involvement in the private noneconomic affairs of citizens. Democrats advocate for the civil rights of minorities, and they support a safety net for individuals, backing various social welfare programs, including Medicaid and food stamps. To fund these programs and other initiatives, Democrats often endorse a progressive tax. In addition, Democrats notably support environmental protection programs, gun control, less-strict immigration laws, and worker rights.
(Encyclopaedia Britannica) "The Democratic Club" artwork by Andy Thomas
The Democratic painting features Andrew Jackson, Franklin Roosevelt, Truman, Kennedy, Lyndon Johnson, Carter and Clinton.
|
Republican Party, byname Grand Old Party (GOP). During the 19th century the Republican Party stood against the extension of slavery to the country’s new territories and, ultimately, for slavery’s complete abolition.
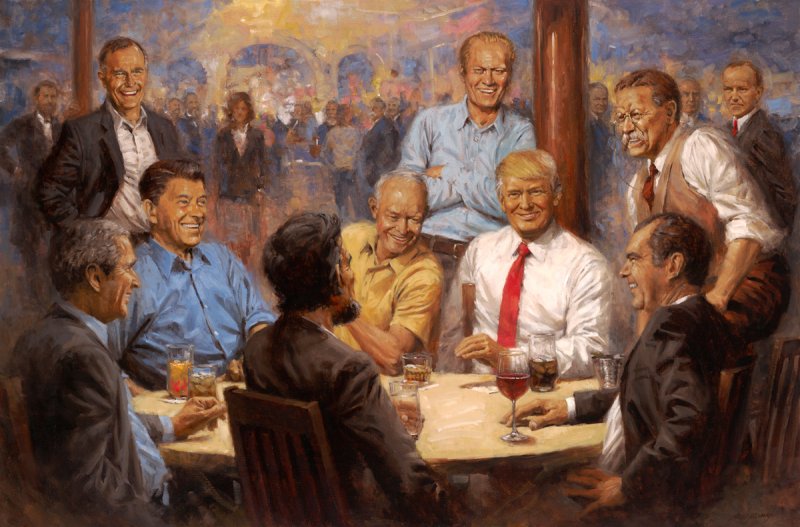
During the 20th and 21st centuries the party came to be associated with laissez-faire capitalism, low taxes, and conservative social policies. The party acquired the acronym GOP, widely understood as “Grand Old Party,” in the 1870s. The party’s official logo, the elephant, is derived from a cartoon by Thomas Nast and also dates from the 1870s. (Encyclopaedia Britannica) "The Republican Club" artwork by Andy Thomas
The fantastical painting shows Trump smiling around a table alongside presidents (some dead, some alive) Ronald Reagan, Abraham Lincoln, Richard Nixon, Teddy Roosevelt, Dwight Eisenhower, Gerald Ford, George H. W. Bush, and George W. Bush.
|